reason
- viral diseases;
- malnutrition;
- lack of physical activity;
- Excess weight, especially in the obesity stage;
- age-related changes;
- drinking, overeating;
- uncontrolled drug use;
- hypertension;
- Other endocrine diseases;
- Pancreatic damage;
- Effects of stress.
symptoms of diabetes
- Frequent urination (polyuria). In diabetes, urine is passed out in large amounts but painlessly, mostly during the day;
- persistent thirst due to dehydration;
- Increased appetite can manifest as attacks in the early stages of the disease. Patients often prefer sweet foods consisting of simple carbohydrates;
- Weight changes. Due to excessive appetite, patients often lose weight due to increased protein and fat catabolism.
- decreased vision;
- numbness in hands and feet;
- Drowsiness (especially during the day), weakness, severe fatigue, increased sweating even with slight exertion;
- Skin problems (itching, non-healing wounds, black bumps on certain parts of the body);
- Dry mouth, inflamed gums, and deterioration of teeth.
type of diabetes
type 1 diabetes
type 2 diabetes
gestational diabetes
- overweight;
- Over 30 years old;
- There is a history of severe poisoning and gestational poisoning, chronic miscarriage, stillbirth, and chronic malformation in children during previous pregnancy;
- Suffering from cardiovascular and endocrine diseases.
risk factors
Other diseases
age
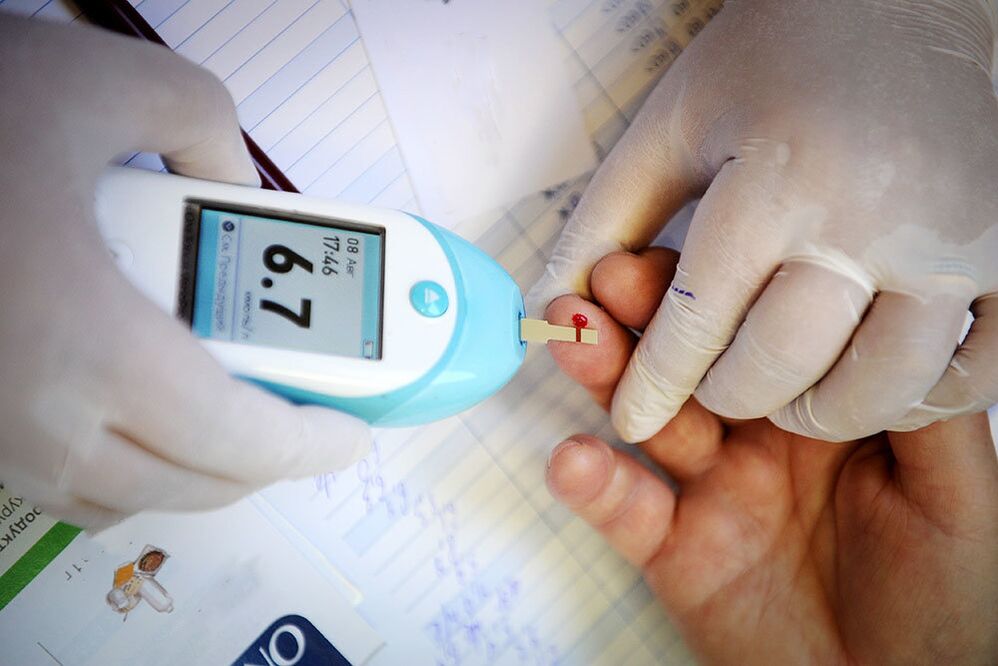
diagnostic methods
diabetes treatment
- Enhance insulin secretion;
- Increase insulin sensitivity;
- Reduced absorption of carbohydrates and other substances;
- diet (a diabetic diet necessarily involves carbohydrate restriction),
- feasible physical activity,
- Compensate for vitamin and trace element deficiencies,
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly.
Possible complications
- retinal detachment;
- kidney failure;
- Neuropathy;
- Atherosclerosis, which causes many serious problems, including angina, heart disease, and stroke.
Prevention of pathology
- Maintain an active lifestyle and control your weight;
- Eat right and reduce consumption of fast carbohydrates (baked goods, sweets, etc. );
- Quit bad habits (smoking, regular drinking);
- Avoid unnecessary stress;
- After age 40, check your blood sugar levels once a year.